Have you ever been shivering on a cold winter morning, wondering how to heat your home? You’re not alone. Central heating systems are essential for those frosty UK winters, ensuring our homes stay cosy and inviting.
There are several types of central heating systems available in the UK. Knowing the differences can help you make an informed decision, especially if you consider changing or setting up a new system.
So, why wait? Keep reading to get a clear understanding of the types of central heating systems and find the perfect fit for your home.
What are Central Heating Systems?
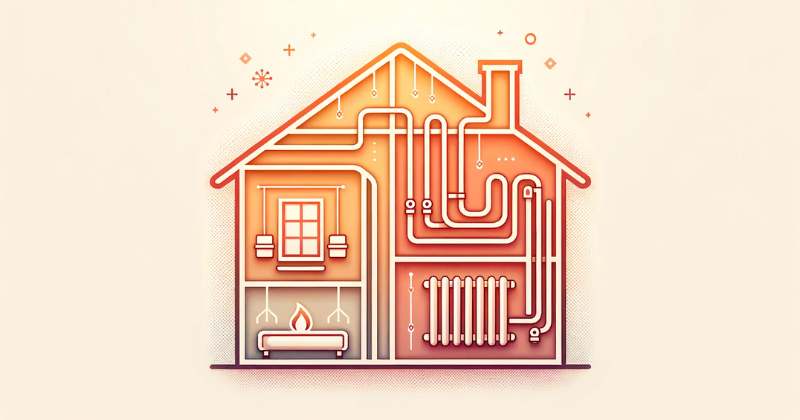
As the name suggests, central heating systems provide a centralised source of warmth for residential and commercial spaces. Instead of relying on individual heaters in each room, central heating offers a more holistic approach.
A central heating system produces heat from one source and spreads it evenly across the entire building.
The beauty of central heating lies in its efficiency. Think of a central heating system as a building’s heart, circulating warmth just as the heart circulates blood.
From quiet countryside cottages to busy city offices, central heating’s goal is consistent: to keep interiors warm, no matter how cold it is outside. With even heat distribution, they offer both comfort and energy efficiency, making them common in UK homes and businesses.
Components of a Central Heating System
A central heating system is like a well-orchestrated symphony, where each component is crucial in ensuring the entire system functions harmoniously.
Every part is interconnected and essential for maintaining a warm and comfortable environment, from the boiler that generates heat to the thermostat that controls the temperature.
Let’s delve into the key components that make up this intricate system.
Heat Source
At the heart of any central heating system is the heat source. This is the starting point, creating the warmth that spreads across your home or office. Common heat sources include
- Boilers: These are water heaters that produce steam or hot water for heating. Various fuels, including gas, oil, or electricity, can power them.
- Heat Pumps: These devices transfer heat from one place to another, making them highly efficient. Even in cooler temperatures, they can extract warmth from the air or ground.
- Furnaces: Typically powered by gas or oil, heat air and distribute it throughout the building.
Distribution Medium
Once generated, the heat needs a way to travel throughout the building. This is where the distribution medium comes into play. Depending on the system:
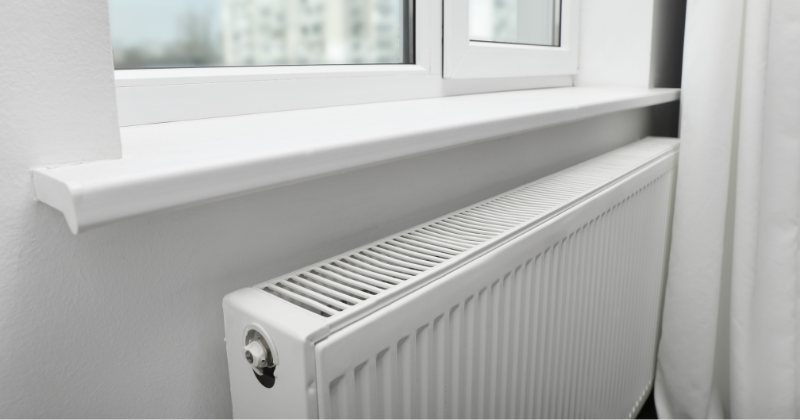
- Water: In systems like radiators, pipes circulate hot water, radiating warmth.
- Air: Forced-air systems push heated air through ducts and vents to warm various areas.
- Steam: Some older systems distribute steam through pipes, condensing it back into water.
Method of Heat Transfer
Heat doesn’t just move independently; it follows specific pathways and methods within a system. Let’s delve into the primary mechanisms:
- Conduction: This is the process where heat travels through a solid material without the material itself moving. Imagine touching a metal spoon that’s been sitting in a hot soup; the heat you feel is transferred through conduction.
- Convection: Heat is transferred through fluids like air or water. As the fluid warms up, it rises, and the cooler fluid takes its place, creating a circulation pattern. It’s the reason why warm air rises, and cool air settles.
- Radiation: Unlike conduction and convection, radiation doesn’t need a medium to transfer heat. It moves in the form of electromagnetic waves. The warmth you feel from the sun, even across the vastness of space, is due to radiation.
Energy Sources
The heart of any central heating system is its energy source, the primary driver that powers the system and provides warmth. The choice of energy source determines the efficiency of a heating system and its environmental impact. Common energy sources include:
- Fossil Fuels: These are the traditional powerhouses, including coal, oil, and natural gas. They’ve been the backbone of our energy needs for decades. However, while they’re abundant and often cost-effective, they come with environmental concerns due to carbon emissions.
- Electricity: A versatile energy source, electricity can power various heating systems, from electric boilers to radiators. Its environmental impact largely depends on how it’s generated – whether from fossil fuels, nuclear power, or renewable sources.
- Renewable Sources: The stars of sustainable energy, renewables like solar and biomass, are gaining traction. Solar panels harness the sun’s energy, while biomass systems burn organic materials like wood pellets. These sources are more environmentally friendly, reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainability.
The choice of energy source is pivotal. It not only determines the efficiency of the heating system but also its environmental impact. Understanding and weighing these considerations becomes crucial in making informed decisions for our homes and the planet as we become more environmentally conscious.
Different Types of Central Heating Systems
In the vast realm of central heating, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Depending on your specific requirements, the size of your space, and even your geographical location, many heating systems are tailored to fit diverse needs.
From traditional boiler setups to innovative underfloor and storage heating systems, the options are as varied as they are efficient. Let’s explore the diverse range of central heating systems available.
Conventional Heating Systems
A nod to tradition, conventional heating systems are the backbone of many UK homes. They operate using a central boiler that heats water, which is circulated through a network of pipes and radiators. As the hot water flows through these radiators, they radiate warmth into the rooms.
Boiler Systems
Boilers are integral to many central heating setups. They come in various types, each with its unique features and benefits.
Combi Boiler
Combi boilers, or combination boilers, are the multitaskers of the boiler world. They provide space heating and instant hot water, eliminating the need for a separate hot water storage tank. This dual functionality not only saves space, making them ideal for smaller homes but also ensures efficient energy use.
System Boiler
System boilers are designed with larger households in mind. They store hot water in a cylinder, allowing multiple taps to run simultaneously without a drop in water temperature. This ensures that hot water is readily available, especially during peak times.
Regular Boiler
Also known as traditional or heat-only boilers, regular boilers work in tandem with both a hot water cylinder and a cold-water storage tank. They are often found in older homes and are particularly suited for properties with multiple bathrooms or where water pressure is low.
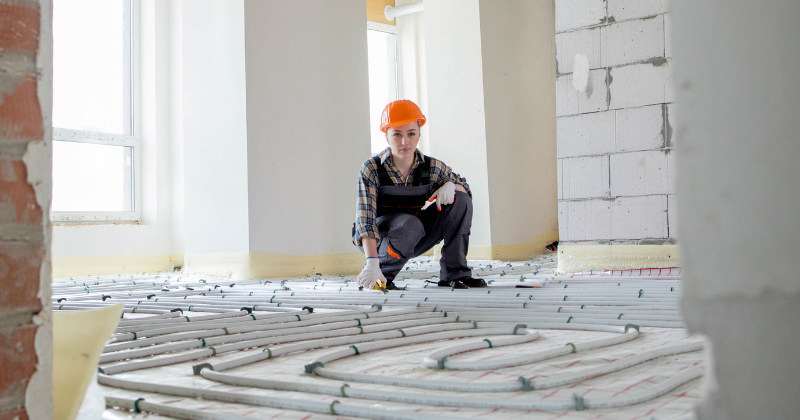
Underfloor Heating Systems
Imagine stepping onto a warm floor on a cold winter morning. Underfloor heating systems make this luxury a reality. Instead of relying on radiators, these systems heat the floor, providing an even distribution of warmth. They’re not only more comfortable but also more energy-efficient, as the heat rises uniformly across the room.
Forced Air Heating Systems
Commonly used in larger buildings, forced air systems heat air and distribute it throughout the building via a network of ducts and vents. The warm air is pushed out of vents, raising the room’s temperature, while cooler air is drawn back into the system to be reheated.
Heat Pump Systems
Heat pumps are the marvels of the heating world. Instead of generating heat, they transfer it. By extracting warmth from the environment, they can provide heating even when it’s cold outside.
Air Source
Air source heat pumps extract heat from the outside air. They’re efficient and work best in moderate climates, making them popular in many UK homes.
Ground Source
Tapping into the Earth’s consistent underground temperature, ground source heat pumps, or geothermal heat pumps, offer high efficiency and reliable performance throughout the year.
Water Source
For properties near water bodies, water source heat pumps come into play. They extract heat from nearby lakes, rivers, or ponds, providing an eco-friendly heating solution.
In conclusion, the new central heating system landscape is diverse, with a solution for every need. Whether you’re looking for the traditional warmth of a boiler or the innovative efficiency of a heat pump, there’s a system waiting to make your home a haven of comfort.
Fuel Types of Central Heating Systems
The fuel type you choose for your central heating system plays a pivotal role in determining its efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. Different fuels offer varied benefits, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision tailored to your specific needs and location.
Gas Central Heating
Natural gas is a popular choice for central heating in many UK homes. Its widespread availability and cost-effectiveness make it a go-to option for many. Gas central heating systems use a gas boiler to heat water, which is circulated through radiators or underfloor heating systems. The combustion of natural gas is relatively clean, producing fewer emissions compared to other fossil fuels.
Electric Central Heating
Electric central heating is gaining traction, especially in areas without gas connections or in smaller spaces. These systems use electricity to heat elements within radiators or boilers. One of the major advantages of electric heating is its ease of installation. There’s no need for flues or pipework, making it a hassle-free option. Moreover, electric heating can be environmentally friendly when sourced from renewable energy.
Oil Central Heating
In areas without a mains gas connection, oil central heating offers a viable alternative. These systems use oil stored in a tank on the property. The oil is burned to heat water, which is then distributed throughout the home. While oil systems are efficient, fluctuating oil prices can impact running costs.
Biomass Central Heating
Biomass heating systems are a nod to sustainability. They use organic materials, such as wood pellets, chips, or logs, as fuel. When these materials are burned, they release the same amount of carbon dioxide they absorbed while growing, making them carbon neutral. Biomass systems reduce dependence on fossil fuels and have a positive environmental impact.
Electric Central Heating Vs Gas Central Heating
The debate between using electric heaters and gas central heating is a hot topic. Both systems have their merits, and the best choice often depends on individual circumstances.
- Cost: Gas is often cheaper than electricity, making gas central heating systems generally less expensive to run. However, electric systems might have lower installation costs.
- Efficiency: Electric radiators can be 100% efficient at the point of use, meaning all the electricity they consume is converted into heat. On the other hand, gas systems might lose some energy through waste gases.
- Environmental Impact: Electric heating can be more eco-friendly when electricity is sourced from renewables. Gas produces fewer emissions than coal or oil but still has a carbon footprint.
- Installation and Maintenance: Electric systems are easier to install and require less maintenance. While more complex, gas systems are tried and tested, with many professionals available for repairs and maintenance.
Check out our article for a detailed reference of electric vs. gas central heating.
Considerations When Choosing Types of Central Heating Systems
Selecting the right central heating system for your home or business is a decision that goes beyond just wanting a warm space. It’s a blend of practical, financial, and environmental considerations. From understanding the climate you live in, to considering the long-term savings, here are some key factors to ponder when choosing.
Climate and Location
Your geographical location and the climate therein play a pivotal role in determining the type of heating system you’ll need. For instance, homes in colder regions might require a more robust and powerful conventional heating system solution to combat the freezing temperatures. In milder climates, a moderate heating system might suffice. It’s essential to choose a system that can efficiently meet the demands of your local weather conditions.
Moreover, climate factors can have a unique influence on certain heating solutions, as highlighted in a study on geothermal resources in SE Poland. It’s essential to choose a system that can efficiently meet the demands of your local weather conditions.
Initial Costs and Long-Term Savings
While the upfront cost of installing a heating system is a significant factor, it’s equally crucial to consider the long-term savings. Energy-efficient systems, though sometimes pricier initially, can lead to substantial reductions in utility bills over time. It’s a balancing act between the initial investment and the potential savings in the long run.
Available Fuel Sources
The availability of fuel sources in your area can significantly influence your heating system choice. For instance, if you live in a region without a mains gas supply, oil or electric heating options become more relevant. It’s essential to understand what fuels are readily available and cost-effective in your locality before making a decision.
Maintenance Requirements
Every heating system, irrespective of its type, requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. However, the frequency and cost of this maintenance can vary. For instance, biomass systems might need more frequent cleaning than gas boilers. It’s essential to factor in these maintenance demands, both in terms of time and cost, when choosing a system.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
In an era where environmental concerns are paramount, the energy efficiency of your heating system is not just about saving money—it’s also about reducing your carbon footprint. Opting for an efficient energy-efficient system can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, renewable energy sources, like solar or biomass, offer sustainable heating solutions that are both efficient and eco-friendly.
In conclusion, choosing a central heating system is a multifaceted decision. Considering the abovementioned factors, you can ensure that your chosen system aligns with your practical needs, budget, and environmental values.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Types of Central Heating Systems
Choosing the right central heating system is more than just a matter of staying warm—it’s about making a well-informed decision that considers your comfort, budget, and the environment.
From understanding the different types of systems and their components to weighing the pros and cons of various fuel sources, it’s clear that there’s a lot to consider. But with the right information at your fingertips, you can make a choice that ensures cosy winters for years to come.
We hope this guide has shed light on the intricacies of central heating systems. If you want to delve deeper into specific electric central heating system solutions, check out our detailed article on electric central heating. And if you have any thoughts or experiences to share, we’d love to hear from you in the comments below.
Stay warm and make informed choices!








Leave a Reply