If you’re reading this, you’re probably considering upgrading or installing a new heating system in your home. With the UK’s unpredictable weather, having an efficient heating system is crucial. But with so many options available, how do you decide which one is right for you? Don’t worry; I’m here to guide you through the basics of the different types of heating systems in the UK. Let’s embark on this toasty journey together!
Central Heating Systems
Central heating systems are the backbone of warmth in many UK homes, providing consistent and efficient heat throughout. But with various options available, how do you decide which one is right for you? Let’s delve deeper into the world of centralised heating systems.
Gas Boilers
Gas boilers are among the most common heating systems in the UK. They operate by burning natural gas to heat water, which is then circulated through radiators or underfloor heating systems to warm your home. The process is efficient, providing on-demand heat when you need it.
Oil Boilers
Oil boilers function similarly to gas boilers but use oil as their primary fuel source. The oil is burned to produce heat, which is then used to warm the home. One of the significant benefits of oil boilers is their efficiency, especially in areas where gas supply might be limited.
However, there are some drawbacks. Storing the oil can be a challenge, requiring a storage tank that can sometimes be an eyesore. Additionally, the price of oil can fluctuate, leading to varying heating costs. It’s essential to weigh these factors when considering an oil-based heating system.
Biomass Boilers
Biomass boilers represent a step towards sustainable heating. They burn organic materials, like wood pellets, logs, or chips, to produce heat. This means they’re using renewable resources, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
In terms of efficiency, biomass boilers can be comparable to gas and oil boilers. They’re suitable for a range of property types, from urban homes to rural retreats. Moreover, using biomass as a fuel source can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are an innovative solution to home heating. There are three main types: air source, ground source, and hybrid.
- Air source heat pumps extract heat from the outside air, even in cold weather.
- Ground source heat pumps, on the other hand, draw heat from the ground.
- Hybrid systems combine the features of traditional boilers with heat pumps for optimal efficiency.
Heat pumps are particularly suitable for the UK’s temperate climate, providing consistent warmth throughout the year. They’re also incredibly energy-efficient, potentially leading to significant savings on energy bills.
The UK offers a diverse range of central heating systems, each with its unique advantages and considerations. Whether you’re looking for an eco-friendly solution or a system that provides consistent warmth, there’s an option tailored to your needs.
Non-Centralised Heating Systems
While centralised heating systems are popular for warming entire homes or buildings, non-centralized heating and hot water systems offer flexibility, targeting specific areas or rooms. Let’s explore these versatile options in more detail.
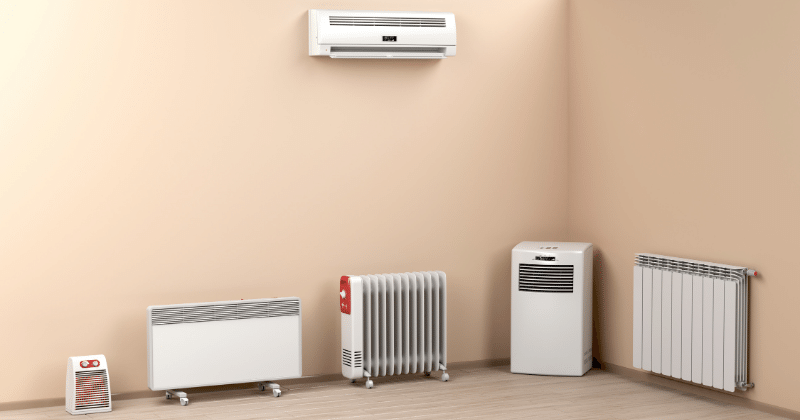
Electric Heaters
Electric heaters have become a popular choice for many homeowners, thanks to their adaptability and the variety of models available. From the gentle warmth of radiant heaters that emit heat using infrared technology to convection heaters that circulate warm air in a room, and fan-forced heaters that blow air over a heat source to spread warmth quickly, there’s an electric heater tailored for every need.
Pros of Electric Heaters:
- Ease of Installation: One of the significant advantages of electric heaters is their plug-and-play nature. Most models simply require a standard electrical outlet, eliminating the need for complex installations.
- Individual Room Heating: Electric heaters are perfect for targeting specific rooms or areas, allowing users to adjust the temperature based on individual preferences. This means you can have a warmer living room while keeping the bedroom cooler, for instance.
- Variety of Options: Whether you prefer the direct warmth of a radiant heater or the even heat distribution of a convection heater, there’s an electric heater designed to meet your specific requirements.
Cons of Electric Heaters:
- Energy Consumption: While electric heaters provide instant warmth, they can be energy-intensive, especially if used continuously. This can lead to higher electricity bills if not managed properly.
- Safety Concerns: Like all electrical appliances, electric heaters need to be used with caution. It’s essential to ensure they’re placed away from flammable materials and that they’re turned off when not in use.
Energy Efficiency and Optimisation Tips:
- Thermostats and Timers: Many modern electric heaters come with built-in thermostats and timers. These features allow you to set the desired temperature and heating duration, ensuring the heater operates only when needed.
- Positioning: Place your electric heater in a location where its warmth can be distributed evenly. Avoid placing it near windows or draughty areas to prevent heat loss.
- Regular Maintenance: Dust and debris can reduce the efficiency of your heater. Regularly clean the heater’s vents and surfaces to ensure optimal performance.
- Use Strategically: Instead of running the heater continuously, use it strategically. For instance, heat a room before you plan to use it and turn off the heater when you leave.
Electric heaters offer a convenient and flexible heating solution, especially for homes that require targeted warmth. By understanding the different types available and following energy optimization tips, you can enjoy the benefits of an electric heating system, while managing energy consumption effectively.
For more on electric heating, check out this guide on electric radiator heating.
Storage Heaters
Storage heaters have been a staple in many UK homes for decades, especially in households looking to capitalise on off-peak electricity tariffs. But how do they work, and are they the right fit for your heating needs? Let’s dive in.
How Storage Heaters Work: Storage heaters are designed to absorb and store electrical energy during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper. They use this stored energy to heat up internal bricks, which then gradually release this heat throughout the day. This approach allows homeowners to heat their homes at a fraction of the cost during peak electricity hours.
Pros of Storage Heaters:
- Cost-Effective: The primary advantage of storage heaters is their ability to operate during off-peak hours, leading to significant savings on electricity bills.
- Ease of Installation: Like electric heaters, most storage heaters are relatively easy to install, requiring minimal disruption to your home.
- Individual Room Heating: Storage heaters can be used to target specific rooms or areas, providing flexibility in heating and allowing for personalised temperature settings.
Cons of Storage Heaters:
- Limited Control: One of the main drawbacks of storage heaters is the limited control over immediate heating needs. Once the stored heat is depleted, you’ll have to wait until the next off-peak period to recharge the heater.
- Bulkiness: Storage heaters tend to be bulkier than other electric heaters due to the internal bricks used for heat storage.
- Heat Loss: If not adequately insulated, storage heaters can lose heat, reducing their efficiency.
Suitability for Specific Situations
Storage heaters are particularly suitable for homes that are unoccupied during the day. The heaters can charge overnight and release heat during the day, ensuring a warm home when residents return in the evening. They’re also ideal for homes in areas with significant differences in peak and off-peak electricity tariffs.
However, for homes with varying heating needs throughout the day or those occupied predominantly during daytime hours, storage heaters might not be the most efficient option. The inability of electric storage heaters to provide immediate heat on demand can be a limitation in such scenarios.
Storage heaters offer a unique heating solution that capitalises on off-peak electricity tariffs. While they provide cost-effective heating for specific situations, it’s essential to weigh their pros and cons against your household’s heating needs. If you’re looking for a heating system that offers both savings and flexibility, storage heaters might be worth considering. However, always assess your daily routine and heating requirements before making a decision.
Portable Heaters
When it comes to quick, targeted warmth, portable heaters are the go-to choice for many. Their compact design and mobility make them a versatile heating solution, especially for homes that require occasional or supplemental heating in specific areas. Let’s explore the world of portable heaters in more detail.
Types of Portable Heaters
- Ceramic Heaters: These heaters use ceramic plates and aluminium baffles. When electricity passes through the ceramic, it heats up and transfers this heat to the aluminium, which then radiates it into the room.
- Oil-Filled Radiators: Despite their name, these heaters don’t burn oil. Instead, they use electricity to heat the oil inside, which then warms the surrounding air. They’re known for providing long-lasting heat.
- Infrared Heaters: These heaters emit infrared light, which is invisible to the naked eye but delivers direct warmth to objects and people in its path.
- Fan Heaters: These heaters use a fan to blow air over a heat source, quickly dispersing warmth throughout a room.
Pros of Portable Heaters
- Flexibility: The main advantage of portable heaters is their ability to be moved from room to room, providing targeted warmth wherever it’s needed.
- Ease of Installation: Most portable heaters simply require a plug socket, making them incredibly user-friendly.
- Variety: With various types available, you can choose a portable heater that best suits your specific needs and preferences.
Cons of Portable Heaters
- Energy Consumption: While portable heaters provide instant warmth, they can be energy-intensive if used continuously or in large spaces.
- Heat Distribution: Some portable heaters might not distribute heat as evenly as centralised systems, leading to hot and cold spots in a room.
- Durability: Given their compact nature, some portable heaters might not be as durable as fixed heating systems.
Safety Considerations: Safety is paramount when using portable heaters. Here are some essential tips:
- Stable Surface: Always place portable heaters on a flat, stable surface to prevent tipping.
- Distance from Flammable Materials: Ensure the heater is positioned away from curtains, furniture, or any flammable materials.
- Supervision: Never leave a portable heater unattended, especially around children or pets.
- Overheat Protection: Opt for models with overheat protection, which automatically shuts off the heater if it gets too hot.
- Regular Checks: Periodically check the heater’s cord and plug for any signs of damage or wear.
Portable heaters are a fantastic solution for those seeking quick and targeted warmth. Their versatility and range make them a popular choice for many households. However, it’s essential to use them responsibly, keeping safety at the forefront. Whether you’re warming up a chilly office or making a bedroom cosier on a cold night, portable heaters can be a valuable addition to your heating arsenal. Just remember to choose the right type for your needs and always prioritise safe usage.
Hybrid Heating Systems
In the ever-evolving world of heating technology, hybrid heating systems have emerged as a frontrunner in combining efficiency with comfort. But what exactly are hybrid heating systems, and how do they differ from the traditional single-source systems we’re accustomed to? Let’s delve into this innovative approach to home heating.
Hybrid Heating: An Introduction
At its core, a hybrid heating system integrates two or more heating technologies to provide optimal warmth and efficiency. Instead of relying on a single source for heat, hybrid systems utilise the strengths of multiple heating methods, automatically switching between them based on specific needs and external conditions. This dynamic approach ensures that the most efficient and cost-effective heating source is used at any given time.
Differences from Traditional Systems
Traditional heating systems, whether they’re gas boilers, electric heaters, or heat pumps, operate independently. In contrast, hybrid systems are interconnected, allowing them to work in tandem and complement each other’s strengths and weaknesses.
Common Hybrid Configurations
Gas Boiler with Air Source Heat Pump
This combination is popular in regions with varying temperatures. During milder temperatures, the air source heat pump operates, providing efficient heating. As temperatures drop, the system switches to the gas boiler, ensuring consistent warmth.
Electric Heater with Ground Source Heat Pump
For homes without access to natural gas, this combination offers an eco-friendly solution. The ground source heat pump provides primary heating, with the electric heater kicking in during peak cold periods.
Biomass Boiler with Solar Thermal Panels
This green combination harnesses renewable energy sources. Solar thermal panels provide hot water during sunny days, while the biomass boiler ensures warmth during colder periods or cloudy days.
Advantages in Different Scenarios:
- Energy Savings: By utilising the most efficient heating source based on real-time conditions, hybrid systems can lead to significant energy savings.
- Environmental Benefits: Combining renewable energy sources, like solar panels or heat pumps, with traditional systems reduces carbon emissions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Over time, the reduced energy consumption can lead to lower utility bills, offsetting the initial investment in a hybrid system.
- Flexibility: Hybrid systems can adapt to changing external conditions, ensuring consistent warmth regardless of the weather.
Hybrid heating systems represent the future of home heating. By combining the best of multiple technologies, they offer a solution that’s not only efficient but also adaptable to a range of conditions and needs. If you’re considering an upgrade or a new central heating system or installation, it might be worth exploring the benefits of going hybrid.
Considerations for Choosing a Heating System That Works for You
Choosing the right heating system for your home is more than just picking the latest model or the one with the most features. It’s about finding a solution that aligns with your home’s characteristics, your budget, and your long-term goals. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate this crucial decision. For insights on cost savings, check out how an electric radiator can save you money.
- Property Size and Layout:
The size of your property and its layout play a pivotal role in determining the type of heating system you need. Larger homes might benefit from centralised systems, while smaller spaces or homes with unique layouts might find non-centralized or portable heaters more effective.
- Insulation:
A well-insulated home retains heat more efficiently, reducing the demand on your heating system. Before investing in a new system, consider checking and upgrading your home’s insulation. This can influence the type and size of the heating system you need.
- Budget:
While it’s tempting to go for the latest and most advanced system, it’s essential to balance this with your budget. Consider both the initial cost of the system and the long-term operating costs. Sometimes, investing a bit more upfront can lead to significant savings in the long run.
- Personal Preferences:
Do you prefer consistent warmth throughout your home, or do you like having different temperatures in different rooms? Your comfort preferences can guide the type of system you choose, whether it’s centralised, zonal, or a combination of both.
- Energy Efficiency Ratings:
Always check the energy efficiency rating of a heating system. Systems with higher ratings consume less energy, leading to reduced utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Look for certifications or ratings that indicate the system’s efficiency. For a detailed comparison between gas and electric heating systems, don’t miss this gas vs. electric heating guide.
- Environmental Impact:
With growing awareness about climate change, many homeowners are considering the environmental impact of their heating choices. Options like biomass boilers, heat pumps, and solar thermal panels are more sustainable and can reduce your home’s carbon emissions.
- Long-Term Maintenance:
Every heating system requires maintenance to operate efficiently. Consider the long-term maintenance requirements, costs, and the availability of service providers in your area.
- Future Needs:
Your current situation might change. You might expand your family, renovate your home, or even move. Think about how adaptable the heating system is to future changes or needs.
Guidance for Evaluation:
- Research: Start by researching different heating systems, their features, and user reviews.
- Consult Professionals: Engage with heating professionals or consultants. They can provide insights based on your home’s specific characteristics.
- Prioritise Needs Over Wants: While it’s great to have advanced features, prioritise your essential needs first.
- Consider Long-Term Value: Look beyond the initial price tag. Consider the system’s lifespan, maintenance costs, and potential energy savings.
Selecting the right heating system is a blend of understanding your home, recognizing your needs, and considering the long-term implications of your choice. By taking the time to evaluate different central heating system options based on the factors mentioned above, you can ensure a warm, comfortable, and energy-efficient home for years to come.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the world of heating systems can initially seem daunting, with its myriad of options and technical jargon. However, by breaking it down and understanding the core principles, you can make an informed decision tailored to your home and needs. Remember:
- Size Matters: Your property’s size and layout are fundamental in determining the right system.
- Efficiency is Key: Always prioritise energy efficiency for long-term savings and a reduced carbon footprint.
- Personalise Your Choice: Your comfort and preferences are paramount. Choose a system that aligns with your lifestyle and comfort needs.
- Think Long-Term: Consider future changes, maintenance costs, and the system’s lifespan.
As you embark on this journey to find the perfect heating solution, remember that the best choice is one that offers comfort, efficiency, and aligns with your values. Interested in diving deeper into the world of home heating? Check out our comprehensive guide on electric radiators for more insights. And if you have any thoughts or experiences to share, we’d love to hear from you in the comments below. Stay warm and make informed choices!








Leave a Reply